Articles by John Tomczyk
From vapor compression to evaporative cooling, R-718 is still a viable option
Read More
The Professor: Global Warming Scares Costing Us Some Popular Refrigerants
Many refrigerants have been delisted in certain applications
Read More
The Professor: The Importance of the Condenser
Condensers perform three vital functions, so keep them clean and damage-free
Read More
The Professor: How Airflow Woes Can Affect Refrigerant Flow
Low suction and head pressures might just be a dirty filter, not a refrigerant undercharge
Read More
The Professor: More Troubleshooting Tips for Spring Tuneups
Properly diagnosing the symptoms is what sets professional technicians apart
Read More
The Professor: In Spring, Thoughts Turn to Troubleshooting
Spotting problems now will help you get a/c systems ready for cooling season
Read More
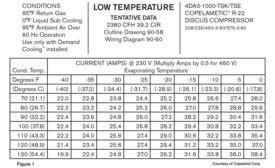
The Professor: Understanding Compressor Amperage Curves
Table-style charts are easy to read and provide valuable information about system function
Read More
The Professor: The Importance of a Refrigeration System’s Operating Pressures
Calculating and analyzing compression ratios can aid system troubleshooting
Read More
Refrigeration Zone
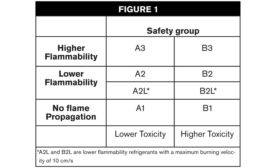
The Professor: The Art and Science of Creating Refrigerant Blends
Each component brings its own characteristics to the final mixture
Read More
The Professor: Calculating Net Temperature Glide
Simple calculations account for system pressure drop
Read More
Copyright ©2025. All Rights Reserved BNP Media.
Design, CMS, Hosting & Web Development :: ePublishing